
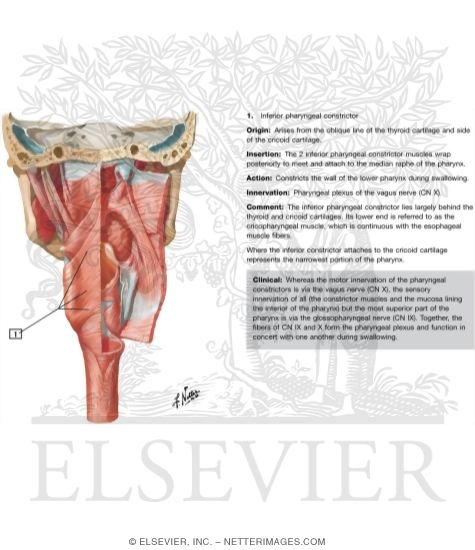
Histologic study of the normal human adult soft palate.

Philadelphia: Harper and Row, 1985, pp 1–9. In: English GM (ed.), Otolaryngology, Vol. Anatomy of the pharynx, pertinent to swallowing. Anat Rec 1989 224:117–122.īosma JF, Donner MW, Tanaka E, Robertson D. Morphology of the pterygomandibular raphe in human fetuses and adults. Morphologic characteristics of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle in relation to the function during swallowing. Tsumori N, Abe S, Agematsu H, Hashimoto M, Ide Y.
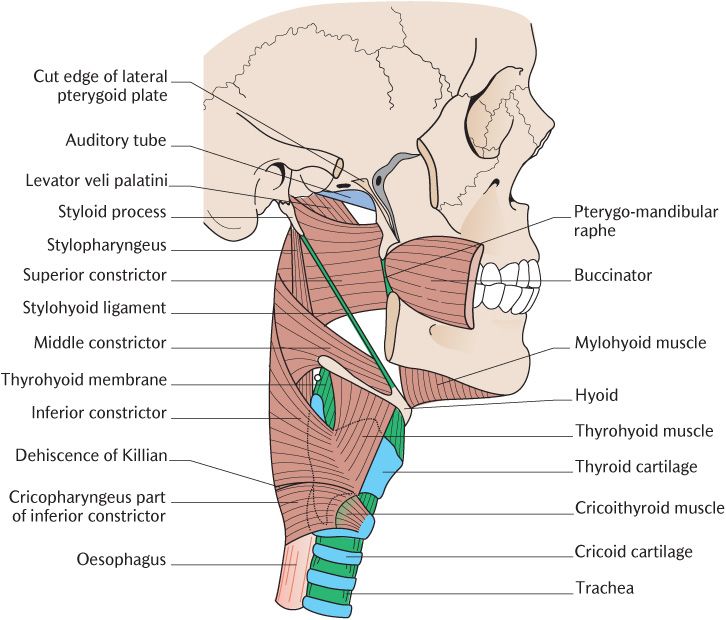
The present results suggest that the palatopharyngeal muscle has a close positional relationship with the levator and tensor muscles of the palatine velum, the pharyngeal constrictor muscles, and the esophagus. In the central pharyngeal wall, insertion into the pharyngeal aponeurosis, inferior constrictor pharyngeal muscle, and esophagus were observed. This insertion was seen in a wide area and could be divided into three parts: the pharynx anterior, central, and posterior walls. When the palatopharyngeal muscle originated from both the oral and the nasal side, it traveled through its insertion via the levator muscle of the palatine velum. However, in some cases the muscle originated on the nasal side was lacked. We found that the origin of the palatopharyngeal muscle was both the oral and the nasal side of the soft palate it was also attached to both the palatal aponeurosis and the soft palate median. In an effort to clarify the morphologic characteristics of the palatopharyngeal muscle, we examined its origin, insertion, and positional relationship with other muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
